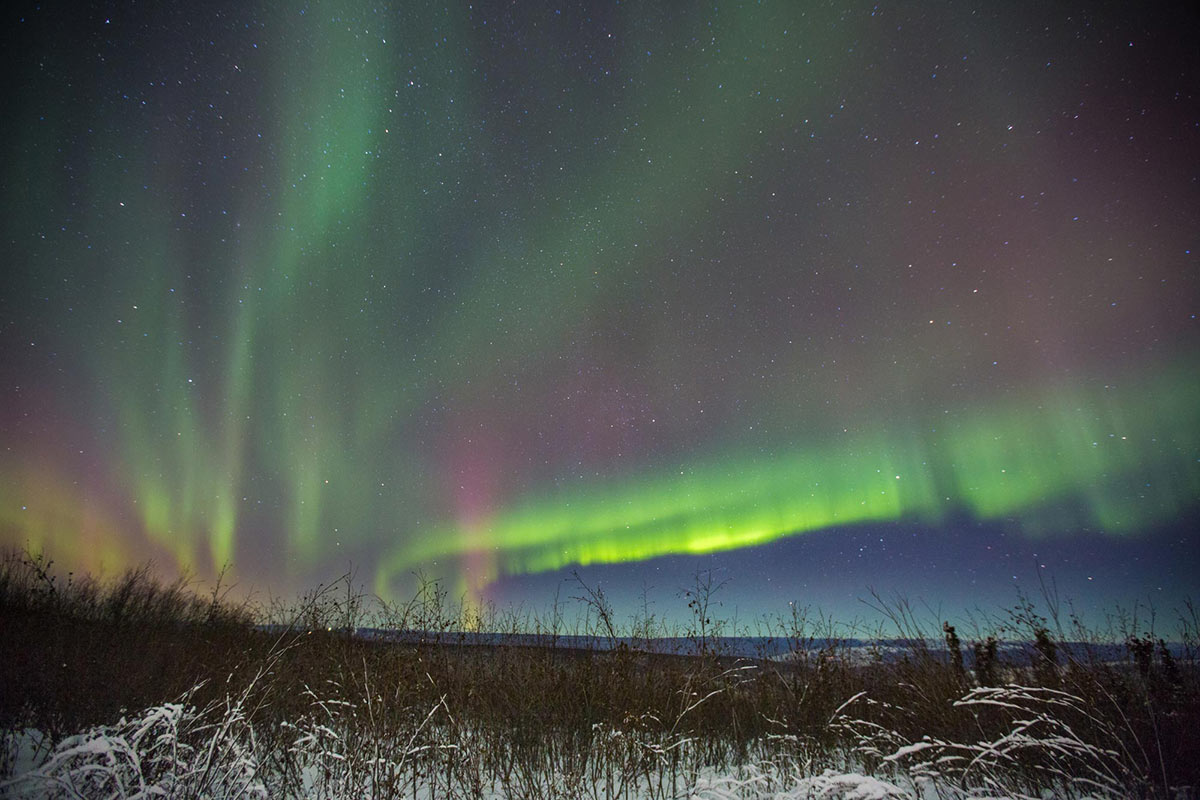
1. Aurora Borealis is a natural phenomenon named after a Greek god and a Roman goddess.
The 17th century astronomer, physicist and philosopher, Pierre Gassendi, saw the Northern Lights on a trip in the North and named them the Aurora Borealis.

Aurora was the Roman goddess of dawn who woke up the world with her torch. She was trailed by maidens who threw flower petals onto the world to ensure the start of a bright new day. The second word, Borealis, Gassendi derived from the Greek god of the north wind—Boreas.
2. Different combinations of elements determine the colors of the Aurora.
When a solar storm (or a magnetic storm on the sun) occurs, electrically charged particles, or ions, are rapidly drawn to the Earth by the its magnetic field. The ions then collide with the earth’s different gases in the upper atmosphere emitting various colors of light. The color of light depends on the type of ion (charged or not) and gas colliding together, and the altitude. Charged ions and nitrogen at a high altitude create a brilliant blue and charged ions that crash into oxygen at a lower altitude become a yellowish-green color, which is the most common color.
As these mesmerizing displays of light known as auroras grace the night sky, scientists and enthusiasts alike gather to witness this natural spectacle. Capturing the essence of both beauty and scientific wonder, auroras continue to fascinate researchers who study the intricate dance of particles and gases that give rise to these celestial phenomena. By delving deeper into the mechanisms behind these colorful light shows, we unveil more mysteries of our Earth’s magnetic field and its interaction with the solar winds, shedding light on the captivating relationship between our planet and the sun.
3. Sometimes the Northern Lights can affect the modern world.
Since the Northern Lights are created by solar activity, the same events from the Sun that causes the aurora often creates more than just a stunning display. During solar storms people have noted radio interference, satellites and other electronic equipment being affected. In extreme cases, a couple of major power blackouts have been blamed on severe solar storms.
During solar storms people have noted radio interference, satellites and other electronic equipment being affected. In extreme cases, a couple of major power blackouts have been blamed on severe solar storms.
In addition to the impact on technology and electronic devices, solar storms triggered by the Northern Lights can also pose risks to astronauts in space. The heightened solar activity increases radiation levels, putting space travelers at a higher risk of exposure to harmful cosmic rays. Space agencies closely monitor these solar events to ensure the safety of astronauts aboard the International Space Station and other spacecraft, taking necessary precautions to shield them from the heightened radiation levels during such periods. Understanding the relationship between the Northern Lights and solar storms is crucial for safeguarding both technology and human life in space exploration.
4. Did you know that the Northern Lights Clap?
Many folktales and legends tell of crackling noises coming from the Northern Lights. Researchers from Aalto University in Finland published a study in 2012 and referred to recorded “clapping” sounds that they correlated to the visual presence of the Northern Lights. According to the study, these sounds were produced approximately 70 meters (230 ft) above ground and originated from solar particles creating geomagnetic disturbances.
These intriguing findings have sparked further interest and exploration into the mysteries of the Northern Lights. Scientists and researchers around the world are now delving deeper into understanding the correlation between the visual spectacle of the auroras and these ethereal clapping sounds. The enchanting nature of this natural phenomenon continues to captivate our imagination, inviting us to unravel more of its mesmerizing secrets hidden in the vast expanse of the polar skies.
5. Earth is not the only place with auroras.
Jupiter and Saturn—the gas giants of our galaxy—inhibit strong magnetic fields due to their gaseous,  unsolid consistency, and during solar storms these fields create massive aurora ovals. Aurora ovals have also been seen on other planets such as Mars, Neptune and Uranus.
unsolid consistency, and during solar storms these fields create massive aurora ovals. Aurora ovals have also been seen on other planets such as Mars, Neptune and Uranus.
The presence of auroras on these various planets highlights the fascinating similarities and differences in their magnetic fields and atmospheric compositions. While Earth, Jupiter, and Saturn boast powerful magnetic fields that generate spectacular auroras, the occurrences on Mars, Neptune, and Uranus offer valuable insights into the diversity of magnetospheres across our solar system. The study of these auroras not only enhances our understanding of planetary atmospheres but also sheds light on the intricate interplay between solar activity and celestial bodies. Further exploration and research into these captivating phenomena promise to unravel even more mysteries of our cosmic neighborhood.
6. The Aurora Borealis has a sister
In Antarctica, there is also an aurora named the Aurora Australis, australis meaning southern. There is no difference in the two light shows—solar storms interfere with their magnetic poles, just on two opposite ends of the planet.
The Aurora Australis, like its counterpart in the north, is a mesmerizing natural spectacle that paints the night sky with vibrant hues of green, purple, and red. Occurring in the southern hemisphere, this celestial dance of light is a breathtaking display of nature’s beauty, captivating all who are fortunate enough to witness it firsthand. Just as the Aurora Borealis has captivated generations with its ethereal charm, the Aurora Australis serves as a reminder of the awe-inspiring wonders that our planet has to offer.
7. Ancients depicted this source of wonder in cave drawings in France.
Cro-magnon paintings in southern france most likely depict the Northern Lights. These paintings go back to 30,000 years before our time. But how did the Cro-Magnons see the Northern Lights from so far away? 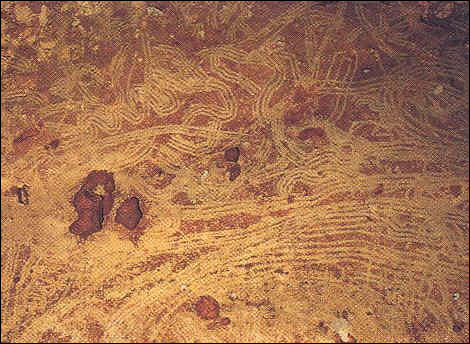 Some would guess that way back then, there was virtually no light pollution.
Some would guess that way back then, there was virtually no light pollution.
The Cro-Magnons’ keen observation of the Northern Lights could also be attributed to their nomadic lifestyle and close connection to nature. Being constantly on the move, they were often situated in remote, open landscapes where the dancing lights in the sky would have been particularly vivid. Additionally, their deep understanding of the environment and celestial patterns might have allowed them to predict and seek out these awe-inspiring natural displays, incorporating them into their cave art as a way to capture and immortalize the enchanting phenomenon that left them in wonder.
8. The Aurora works in cycles.
Everything has its own rhythm and cycle, and the solar activity that causes the stunning displays of the northern lights occur roughly every 11 years (10.66 to be exact). Since its discovery in 1849 by a German astronomer, scientists have compiled observations throughout the centuries and have dated solar cycles back to 1699. Since then, there have been 29.5 cycles. The next strongest peak of the cycle is in 2015-2016!
This upcoming peak is highly anticipated by astronomers and skywatchers alike, as it presents a unique opportunity to witness the magnificent dance of the auroras in the night sky. As the sun reaches its maximum level of activity, sending out intense bursts of solar energy, the Earth’s magnetic field interacts with these charged particles, creating the colorful displays known as the aurora borealis. During this peak, the auroras will be more frequent and vibrant, painting the sky with breathtaking hues of green, pink, and purple. Enthusiasts and scientists around the globe are eagerly preparing for this celestial spectacle, ready to capture and study the beauty and wonder of the northern lights at their most dazzling.
9. Never Miss the Northern Lights!
Several agencies, such as NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, monitor solar activity and issue aurora alerts when they are expected to put on a particularly impressive Northern Lights Show. Learn more about what to pack When preparing for a Northern Lights Alaskan tour, remember to pack warm layers, sturdy footwear, and a camera to capture the breathtaking aurora displays against the Arctic night sky.
If you’re lucky enough to witness the Northern Lights, you’ll be treated to a mesmerizing display of colors dancing across the night sky. The vibrant hues of green, purple, and pink create an otherworldly atmosphere that is truly unforgettable. As you stand in awe of this natural phenomenon, don’t forget to soak in the silence of the Arctic wilderness around you. The stillness of the snowy landscape adds a sense of peace and tranquility to the experience, making it a moment you’ll cherish for a lifetime. Be sure to take a moment to breathe in the crisp, cold air and appreciate the beauty of nature at its most magical.




